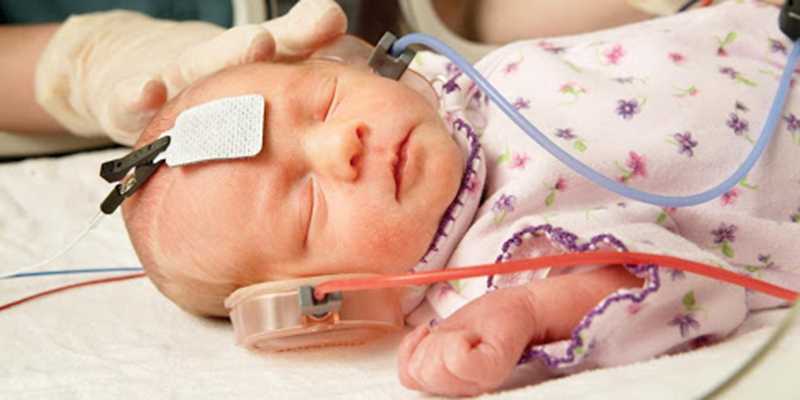
Infants and young children who have not passed the re-screening should receive audiology and medical evaluation at the age of 3 months to ensure that the presence of congenital or permanent hearing loss is determined within 6 months of age for intervention. Children who fail the re-screening should undergo otolaryngology examination and acoustic immittance, otoacoustic emission, auditory brainstem evoked potential testing, behavioral audiometry and other related examinations by hearing testing institutions. Medical and imaging should be performed if necessary Learn to evaluate and make a diagnosis.
For children with high risk factors for hearing loss, the time and frequency of individualized hearing reassessment should be established according to the possible delayed hearing loss. For infants and young children who have passed the newborn hearing screening but have high risk factors for hearing loss, at least 3 years of age, every 6 months, hearing follow-up, if hearing loss is suspected, audiology evaluation should be performed in time.






